We remain open for you!
Dear patients,
we kindly ask you to cancel your appointments in case of flu symptoms or, if possible, to change them to a video consultation.
We will try to arrange new appointments for you as soon as possible.
Please understand these measures. It is for the protection of everyone. Of course, we are there for you by phone as well as by e-mail in such a situation.
Your team at the Fertility Center Berlin
The desire to have our own child is part of our humanity.
The team at the Fertility Center Berlin is open to all people who wish to have children.
We care for heterosexual and same-sex couples, single women and transgender people with their desire to have children. Also couples with chronic infections, couples with cancer before chemotherapy and women who wish to have a fertility prophylaxis (so-called “social freezing”).
Your doctors from the Fertility Center Berlin

Your Fertility Center Berlin Team
Individual care
Our personal care for patients and couples by our doctors has always been a matter of course at our centre. The doctor you trust accompanies you during the diagnosis and treatment period personally and remains your contact person. An unfulfilled desire to have children can be a great burden; therefore, our fertility team is supported competently and sensitively by our psychologists. Please take a look at our team.
Successful treatment
Our pregnancy and birth rates after IVF/ICSI treatment or after a Kryotransfer are well above the national average (German IVF Register). Our success is based on more than 20 years of cooperation between experienced doctors, biologists and the entire medical staff. Our aim is to achieve the best possible therapeutic outcome for our patients, without any burdensome or ineffective additional measures. Please take a look at our statistics.
Caring according to scientific standards
Infertility treatment has developed very positively in recent years. Our pregnancy rate is about 40% per transfer (link). For this high pregnancy rate we work in the laboratory for 7 days using the latest technologies such as embryoscope, vitrification and polar body diagnostics. Since 1999, as the Fertility Center Berlin, we have been continuously involved in national and international research in order to improve the quality of reproductive medicine and to be able to successfully care for our patients at the cutting edge of medicine.
Location
The Fertility Center Berlin, as an owner-managed MVZ, is located on the grounds of the DRK Kliniken Westend in Berlin-Charlottenburg. Our patients benefit from the close cooperation with the colleagues of the gynaecological clinic when operations such as laparoscopies, uterine endoscopies, removal of myomas or endometriosis treatments are necessary, as well as for obstetric issues. Feel free to take a look at the Endometriosis Centre.
Meet our team
The Fertility Center Berlin is a fertility practice. For us as a team, this means that we take care of the needs of people who want to become parents in a competent but sensitive way. And we hope that this attitude of Fertility Center Berlin will always be present for you. By the way, the best way to get to know us is our regular information evening.
Desire to have children

Am I infertile? And when do you speak of it?
The desire to have our own child is part of our humanity, and if it “doesn’t work“, we need some thing above all: helpful information and education. And secondly: good solutions.
Infertility is defined when a pregnancy does not occur even after one year of regular sex by a couple. This view is also shared by the WHO (World Health Organisation), which thus takes into account the changed living conditions in western industrial nations, e.g. the greater mobility of partners. The causes of infertility are manifold in both men and women; 20%-30% related to the woman, 50% to the man and a further 20% in both the man and the woman. In 10%-15% of all couples, the cause of infertility remains unexplained. Infertility treatment is therefore always therapy in both.

Above-average success rates at the Fertility Center Berlin
The success of fertility treatment depends primarily on the experience of the treating doctors and the laboratory. The Fertility Center Berlin team has been working together in the same constellation since 1999. The doctors have known each other since 1991 and have already carried out infertility treatment at the University Women’s Clinic of the FU Berlin (Pulsstraße location) and at the DRK Kliniken Westend.
Risks associated with fertility treatment
No successful treatment is without risks – also the case with fertility treatment. The risks are mainly due to the hormone stimulation and its consequences. Hormone stimulation is usually necessary for successful fertility treatment. This leads to follicle growth and can, in rare cases, lead to overstimulation. Overstimulation is accompanied by enlarged ovaries, fluid formation in the abdomen and more or less pronounced lower abdominal discomfort. In rare cases, it can also lead to shortness of breath or thrombosis. Overstimulation is very rare in the field of conventional sterility therapy (hormone stimulation or insemination). It occurs most frequently with stimulation for in vitro fertilisation (IVF) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). If you experience overstimulation, a gynaecologist should always be consulted for an assessment.
Another risk of treatment is the development of multiple pregnancies. A higher-grade multiple pregnancy (triplets or higher) is very rare and occurs in <1% of all cases after conventional fertility treatment. After in vitro fertilisation (IVF), this has also become more rare in recent years, as only 1-2 embryos are usually transferred in women under 40. Even in women over 40 only 2 embryos should be transferred. Other risks such as the formation of abscesses or the development of bleeding after procedures such as vaginal follicle puncture are very rare and occur with a frequency of about 1:500.
In children born after the ICSI method, the probability of malformation is 9%. In the spontaneously conceived group the probability was 7.2%. Thus, a slightly increased risk of malformation after ICSI can be assumed. However, this risk is only increased to a very limited extent and does not represent a contraindication against fertility treatment.
An unfulfilled desire to have children background of the woman?
Only 30% of the causes of an infertility lie with the woman alone. In 50% of cases the man is involved, in another 20% there is a cause in both. The Fertility Center Berlin supports you in clarifying the causes in your personal case. We discreetly discuss all questions together, carry out a diagnosis and, if necessary, develop a treatment plan for you – in close cooperation with specialists or the doctor you trust.
Possible causes in women:
- Blockage of the fallopian tubes (tubal sterility)
- Uterine endometrioses (endometrium outside the uterine cavity)
- Hormone disorders with too much male hormone and lack of ovulation (PCO syndrome)
- Premature aging of the ovaries
- non-functioning of the pituitary gland with lack of stimulation of the ovaries
- and many other causes.
In our experience, a high proportion of the causes lie in premature depletion of the ovaries, which in individual cases can occur at an early age. However, in many women from the age of 38, this depletion of the ovarian reserve is increasing. This can be measured using the anti-mullerian hormone (AMH), which gives a background to what extent the ovaries are still functional and how good the chances of fertility treatment are.

An unfulfilled desire to have children background of the man?
In about 50% of the causes of an infertility lie with the man. But in any case it is good to use the possibilities of the Fertility Center Berlin: We talk about the possible causes with you, carry out an exact diagnosis and then research the causes – and develop your treatment plan in cooperation with specialists.

Possible causes in men:
- Hormone imbalances
- Varicose veins in the testicles
- Positional anomaly of the testicle
- Mumps disease in childhood
- Diabetes meelitus
- Operated tumours
- Genetic causes
- Infections
- Drug and alcohol abuse
The most common cause of infertility in men is reduced sperm quality. There can be many reasons for this, including the following:
Limited sperm quality
There are different forms of impaired sperm quality: oligozoospermia, asthenozoospermia, teratozoospermia, cryptozoospermia and azoospermia. These can occur individually or in combination with each other.
- Oligozoospermia: The number of sperm in the ejaculate is too low (norm: > 15 mill. sperm/ml).
- Asthenozoospermia: The motility of the sperm is reduced (norm: > 32% motile sperm).
- Teratozoospermia: There are too few normally shaped sperm in the ejaculate (norm: >4% normally shaped sperm).
- Cryptozoospermia: Only isolated sperm are present in the ejaculate.
- Azoospermia: The ejaculate contains no sperm at all.
Treatment
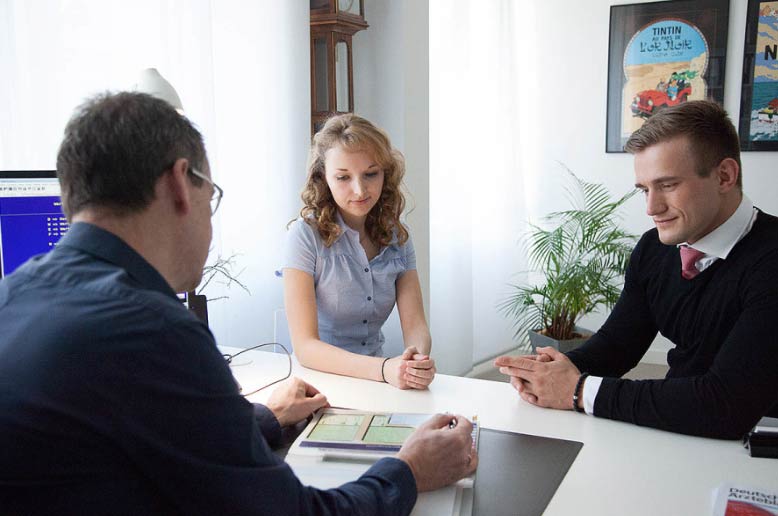

1. Initial conversation
Our aim is to show you the various options for infertility treatment during your initial consultation with one of our doctors. We will advise you about the causes of infertility, the various treatment options, their chances of success, possible risks and financial aspects. It is very important for us to provide you with individual care and advice.
If possible, you should make your first appointment with your partner. It is important that you take enough time; you should plan about one hour for the first appointment.
-
You should bring this with you to your appointment:
- Referral slip from the gynaecologist (private patients do not need a referral slip).
- Health insurance card of the woman
- If available, findings of your gynaecologist (e.g. cancer screening, hormone values, surgery reports)
- Completed questionnaire for the woman
- Health insurance card (man)
- if available, the findings of your treating urologist/andrologist (man)
2. Diagnostics
After this initial consultation, a series of examinations will take place, starting with an appointment for blood sampling and ultrasound examination. The time for this depends on the day of your cycle. The 1st cycle day is the first day of your menstrual period.
An important hormone is the anti-mullerian hormone (AMH): this can be used to directly measure the amount of eggs still present in the ovary. This is important both to give you an estimate of your chance of still getting pregnant and to determine how much hormone stimulation you will need. Unfortunately, the costs for this hormone investigation are not paid for by the health insurance companies, but it makes medical sense.
Further necessary examinations may then take place. These include a physical examination, cycle diagnostics (ovulation), ejaculate analyses (spermiogram) of the partner, tube diagnostics (function of the fallopian tubes) as well as hormone and ultrasound examinations (clarification of egg maturation).
3. Consultation and planning
After all examination results are available, a discussion appointment is held. At this discussion, the options for further therapy are presented and the medically appropriate therapy is recommended.
-
Possible therapies:
Hormonal stimulation & insemination (sperm)

The stimulation of the ovaries begins at day 2 – day 5 of the cycle. A control examination by ultrasound then takes place again after 6 to 8 days. When the follicles have grown to an optimal size, a trigger injection with HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) is given. 36 hours after this injection, ovulation usually takes place. If sexual intercourse is planned, it should take place 24-32 hours after the trigger injection.
In the case of insemination with the partner’s sperm or using donor sperm, the same pre-treatment is carried out as with hormonal stimulation. 24-32 hours after the trigger injection, the partner delivers his semen at the Fertility Center Berlin. The preparation takes about 1.5 hours. This is followed by a normal gynaecological examination, during which the semen is introduced into the uterus using a small catheter (intrauterine insemination).
IVF / ICSI treatment (in vitro fertilisation with or without microinjection (ICSI) of a single sperm into the egg)
In the case of in vitro fertilisation, e.g. using the so-called long protocol, we start administering hormone-regulating medication between the 20th and 22nd day of the cycle (nasal spray or injection of the medication). The first examination then takes place about 14 days later. Alternatively, stimulation can take place from the 2nd or 3rd day of the cycle as with hormonal stimulation.
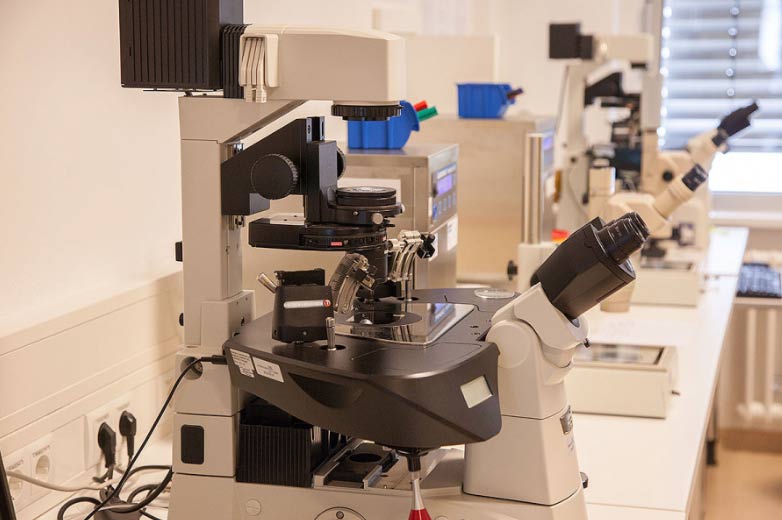
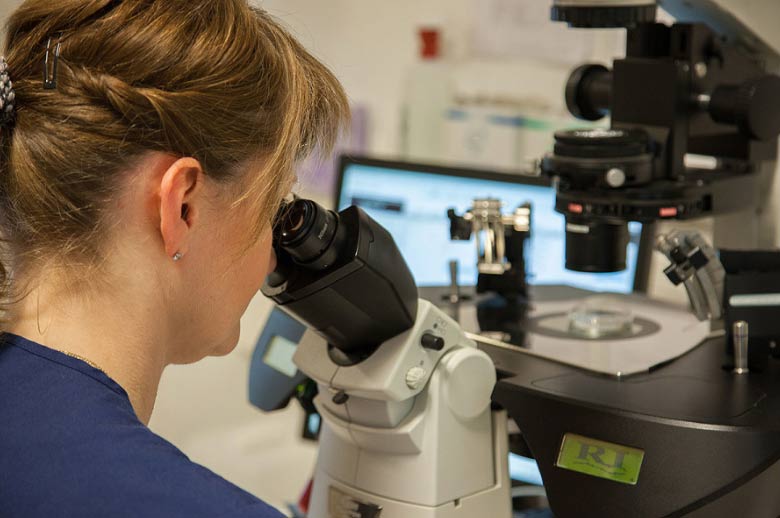



After about 8 to 9 days, another check-up takes place. In order to be able to determine the optimal follicle size, blood samples and ultrasound appointments are arranged at intervals of 2 to 3 days. When the optimal size is reached, ovulation is induced between 8 – 12 pm. The follicle puncture (egg collection) takes place 2 days later. The fertilised eggs are then cultivated in the incubator for 2 – 5 days.
Since 2013, embryos can be observed with the embryoscope at the Fertility Center Berlin. The embryoscope is an incubator with a camera in which 9 pictures of the egg/embryo are taken every 15 minutes and thus the growth is continuously recorded in a time-lapse film. In standard cultivation, on the other hand, the oocytes and embryos may only be taken out of the incubator once a day for checking, so as not to impair the culture conditions and thus the ability to develop. Therefore, the embryologist only has a snapshot available to assess embryo development.
If an limited number of embryos is cultivated in accordance with the liberal interpretation of the Embryo Protection Act, we achieve an increase in the pregnancy rate of approx. 5-8 % per transfer by using the embryoscope, compared to cultivating the embryos in a standard incubator without a camera. This is in line with international data.
Thus, from 2013 – 2018, we achieved a pregnancy rate of 51 % after the return of two embryos in the embryoscope compared to 46 % in the standard incubator and of 42.9 % after the return of only one embryo cultivated in the embryoscope compared to 36.2 % in the standard incubator. The costs for the cultivation of the embryos are not covered by the health insurance and amount to 740 €. The embryo transfer into the woman’s uterine cavity can then take place on day 2, 3 or 5 after the egg collection. The first pregnancy test: please do not take a test from your urine, as this could be falsified!
The result of the pregnancy test will be communicated to you by telephone by a doctor. If the result is positive, the test will be checked after 2 – 5 days, again by taking a blood sample.
However, the further course of the pregnancy cannot yet be predicted. If there is a good increase in the pregnancy hormone HCG, an ultrasound check is carried out after a further 14 days; if the pregnancy is intact, you will then be referred back to your gynaecologist for further prenatal care.
All treatment options at a glance



Cycle monitoring and hormone stimulation treatments in women
If the basic diagnosis has revealed an abnormality in the cycle, which disturbs egg maturation, ovulation and also the further course of the cycle, hormonal stimulation of the cycle can be the first therapy. The aim of hormone stimulation (Clomiphene, Letrozole or FSH) is to optimise the development of an egg within a follicle.
Under ultrasound and hormone controls, the development of the follicle is documented and ovulation is triggered. In this way, the optimal time for sexual intercourse is determined.
Partner sperm treatment (homologous insemination)
Intrauterine insemination (IUI) can be the appropriate method for achieving a pregnancy if there is slightly limited sperm quality and / or anatomical abnormalities in the woman. The pre-treatment in the woman can take place in the spontaneous cycle or also after hormone stimulation.
After ovulation has been triggered, the time for the IUI is determined. The IUI procedure is similar to a gynaecological examination. You are allowed to get up immediately and can go about your daily life normally. The IUI can be carried out with sperm from your partner or with donor sperm.
Fertilisation outside the body (in vitro fertilisation = IVF) and/or injection of the sperm into eggs (intracytoplasmic sperm injection = ICSI).
In vitro fertilisation may be the appropriate method for obtaining a pregnancy if the cause is an obstruction of the fallopian tubes, endometriosis or if there is a PCO syndrome in which pure stimulation does not lead to a pregnancy and in the case of so-called idiopathic sterility, i.e. if the cause remains unexplained.
If the cause is in the man with more severely impaired sperm quality, the appropriate method for achieving pregnancy is in vitro fertilisation in combination with injection of a sperm into the egg (ICSI). The preparations for both IVF and ICSI treatment are the same.
ICSI after sperm collection from the testis in cooperation with urologists/andrologists (testicular sperm extraction, TESE)
If there are no sperm at all in the ejaculate, it is possible to obtain sperm directly from the testicles (TESE = testicular sperm extraction) or epididymis (MESA = microsurgical epididymal sperm aspiration). This is carried out in cooperation with specialised andrologists/urologists.
Donor sperm treatment (donor insemination, donor IVF)
The treatment of donor sperm offers couples a treatment option if the partner has no sperm, e.g. congenital, after illnesses or treatments such as radiotherapy or chemotherapy. For homosexual couples and single women, the treatment with a donor sperm source is a possibility to fulfil the desire to have a child.
We will be happy to advise you on any questions you may have about the treatment of donor sperm. We can also advise you on the choice of sperm banks. Legal advice and psychosocial counselling should be provided prior to donor sperm treatment.
On 01.07.2018, the Sperm Donor Registry Act came into force. We are obliged to report the birth of a child conceived and born with donor sperm treatment to this register. The aim is to ensure that donor children can know their biological origin. The health insurance funds do not cover the costs of the donor sperm banks. With donor sperm, insemination and fertilisation of the egg outside the body (IVF) are possible.
Embryoscope (possibility to continuously assess the development of fertilised eggs)
The embryoscope is one of the new and most advanced ways worldwide to continuously record the development of fertilised eggs (embryos). At the same time, the culture system allows the fertilised oocytes to develop under constant environmental conditions from the very beginning. Temperature, pH value and the supplied gas mixture of air and CO2 are kept in an optimal ratio for the egg cell.
This creates culture conditions that are very close to the natural situation in the body. Here, as almost always in medicine, the principle applies: the closer something can be brought into line with natural conditions, the more optimal the success of the treatment can be.
The built-in microscope allows continuous observation of cell development without having to remove the eggs. This is the only way to avoid disturbances that would otherwise have an unfavourable effect on embryo development.
Compared to the previous situation, there are thus more favourable conditions in suitable cases that can enable an improvement in the pregnancy rate. The results of our continuously conducted evaluations of the pregnancy rates of comparable treatments prove an increase, depending on the age group, of approx. 5 % to 10 % with cultivation in the embryoscope compared to standard cultivation.
Late embryo transfer on day 5 or 6 (blastocyst transfer)
Less than half of the fertilised eggs have the ability to develop into an embryo that can lead to pregnancy and birth. Many embryos die in the first two days in the incubator, so that they are no longer available for transfer into the uterus.
However, if the fertilised eggs develop into good quality embryos, the woman will have a higher pregnancy rate if 1 (at most 2) embryo(s) is (are) transferred not on day 2 or 3, but at the blastocyst stage on day 5. However, this must be in accordance with the Embryo Protection Act in Germany, which prohibits storage fertilisation. However, it is possible, through careful monitoring of the oocytes, pronuclear stage cells and embryos, to allow women the option of blastocyst transfer without coming into conflict with the law.
Our aim is to be able to carry out a transfer on day 5, because this is when the pregnancy rate is highest for you, especially in conjunction with the embryoscope. Of course, the cultivation to the blastocyst on day 5 or 6 with us is not associated with any additional costs for you.
Freezing of fertilised oocytes in the pronuclear stage and of sperm (cryopreservation)
In the course of fertility treatment by IVF or ICSI, more eggs are often produced in the so-called pronuclear stage (impregnated eggs). Since a maximum of 2 to 3 embryos should be created for return in a fresh IVF or ICSI attempt, surplus eggs in the pronuclear stage can be frozen (so-called cryopreservation).
This option opens up additional embryo transfers, as the statutory health insurance funds usually only cover 3 attempts. If a supernumerary blastocyst is produced during cultivation into a blastocyst on day 5, this can also be cryopreserved. The vitrification method used in cryopreservation achieves a survival rate well above 95%.
Cryopreserved pronuclear stages or embryos can be transferred back into the uterus in a later cycle without hormone stimulation. However, the statutory health insurance funds do not cover the costs of freezing, subsequent storage or the transfer cycle. The pregnancy rate at Fertility Center Berlin after transfer of thawed oocytes or embryos is just as high as in the fresh transfer cycle.
Fertiprotection
Fertility-preserving protection in women with cancer:
Facing a malignant disease is an enormous burden. Fortunately, today the treatment options for malignant diseases have improved considerably, so that fertility preservation has a rightful place before starting treatment for a tumour disease.
We will advise you on how and in what measures the tumour treatment can damage the ovaries and on the possibilities of fertility-preserving measures.
After a short hormonal stimulation treatment, oocytes can be brought to maturation and these can be cryopreserved (deep-frozen) after retrieval. For couples with the desire to have children, it is also possible to fertilise the retrieved oocytes immediately and thus freeze the fertilised oocytes.
The freezing of ovarian tissue during a laparoscopy is another option for fertility protection. This ovarian tissue can later be surgically replaced, so that a spontaneous pregnancy is quite possible.
Fertility preservation in male cancer:
In the course of cancer, chemotherapy or radiation can destroy the sperm-forming germ cells in a man’s testicles. Then freezing the sperm sample is possible.
From July 2021 onwards freezing of eggs, sperm or testicular tissue in case of cancer or a serious disease is covered by the statutory health insurance in Germany.
KBB Kryobank Berlin GmbH
Dr. med. R. Andreeßen
Reinickendorfer Straße 15, 13347 Berlin
Tel.: 030 – 495 00 231
Mail: info@krobank-berlin.de
Charité Klinik für Urologie – Kryobank
Dr. Ina Wilkemeyer/Waldemar Geiger
Seestraße 13, 13353 Berlin
Tel.: 030 – 450 615150
Mail: andrologie-labor@charite.de
Freezing of unfertilised eggs (so-called social freezing)
Cryopreservation (deep freezing of unfertilised eggs and sperm) to preserve fertility has been a safe procedure for many years.
Fertility preservation for women:
The reasons why women and men choose this route, which is also called “social freezing”, are varied and are often due to personal circumstances and professional challenges, as well as the fact that fertility declines due to age.
It is known that fertility decreases year by year in many women from the age of 35 onwards, and with it the lower likelihood that healthy eggs will mature.
We take your wish to cryopreserve your unfertilised eggs very seriously. It is important for you to know in advance how well your ovaries can still respond to hormonal stimulation so that enough eggs can be obtained. Factors such as age, cycle, ovarian reserve and anti-mullerian hormone play an important role here. Since not every egg is vital and can be fertilised at a later date, and since not every fertilised egg develops into a healthy embryo, at least 15, preferably 20 eggs should be retrieved. Depending on the individual situation, several stimulation cycles are sometimes necessary. The retrieved eggs can be treated at a later stage in an extracorporeal injection (ICSI).
The costs for the treatment are not covered by health insurance and are around 4000 € including medication, stimulation, egg retrieval, freezing and anaesthesia. The costs for the later necessary extracorporeal fertilisation (IVF) are also not covered by the health insurance. We will give you honest advice on whether social freezing makes sense for you and what opportunities this fertility-preserving measure can offer you.
Fertility preservation measures for men
Cryopreservation of sperm:
It is possible to have your sperm cryopreserved with us. It is often necessary to make several appointments in order to be able to freeze a sufficient amount of sperm. The freezing and thawing process can possibly lead to a loss of sperm movement. Health insurance companies usually do not cover the costs of cryopreservation or storage.
Counselling and treatment for chronic infectious diseases (hepatitis B, C, HIV) in connection with the infertility treatment
Chronic infectious diseases such as hepatitis B, hepatitis C and HIV can have an impact on one’s own health, but also on pregnancy and the child that is eventually born.
At the beginning, the infectious disease and the previous therapy must be precisely recorded. Then, in most cases, a proposal for fertility treatment can be made.
Assisted hatching (laser treatment of embryos)
Incising the outer shell of the embryo, for example with a laser, to facilitate implantation of the embryo in the lining of the uterus.
Polar body diagnostics (PKD), i.e. genetic testing of all 23 maternal chromosomes.
This makes it possible to reduce miscarriages after IVF or ICSI (useful for women from the age of 38 and for couples with a tendency to miscarry).
Polar body diagnostics is an examination method on oocytes that can be used to detect genetic disorders. In principle, it is possible to detect both genetic changes (hereditary diseases) and chromosomal changes (maldistributions and translocations) with this method. For certain groups of patients, the use of polar body diagnostics improves the probability of having a child (e.g. women over 38, women with a tendency to miscarry).
Surgical treatment of women with tubal obstruction (tubal sterility), fibroids, malformations of the uterus, cysts of the ovaries or endometriosis in close cooperation with the gynaecological clinic of the DRK Kliniken Westend on the same premises.
We cooperate with the Department of Gynaecology in many areas, especially in the treatment of tubal occlusions, opening of fallopian tubes, removal of myomas and also especially in surgical treatments that become necessary in the case of endometriosis.
In case of endometriosis, a laparoscopy is usually advised, especially as the chances of a spontaneous pregnancy increase significantly after the treatment of endometriosis. Our centre cooperates here with the endometriosis consultation of the DRK Clinic in Berlin.
Acupuncture and Traditional Chinese Medicine in collaboration with Dr. Diezmann-Wikowski.
Accompanying acupuncture treatment and/or therapy with Chinese herbs can have a supportive effect during fertility treatment. Dr. Sandra Diezmann-Wikowski, a specialist in anaesthesia with an additional qualification in acupuncture, is available to support you during fertility treatment.
Link: http://www.diezmann-wikowski.de/
Fertility diagnostics in women
- Hormone analysis
- Ultrasound examinations
- Examinations for inflammation of the genitals
- Special examinations in women after frequent miscarriages (recurrent abortions)
- Ultrasound examination of the fallopian tubes with contrast medium (hysterosalpingo-contrast sonography)
- Examinations for genetic causes of infertility in women and men (chromosome analysis) in cooperation with Geneticists.
Fertility diagnostics in men
- Semen analysis (spermiogram)
- Hormone analysis
- Examination of the seminal fluid for inflammation and antibodies
-
Treatment costs
To give you an idea of the costs for artificial insemination, among other things, that you will incur in each individual case, we list the individual items here and keep the data up to date.
For couples with statutory health insurance:
Since 01.01.2004, patients with statutory health insurance have had to pay their own share of the costs for reproductive measures. This entitlement to partial cost coverage for these measures by the statutory health insurance funds only exists for married heterosexual couples. Both partners must have reached the age of 25; the entitlement ends for the woman when she reaches the age of 40 and for the man when he reaches the age of 50.
We will show you approximately how much you should expect to pay:
- Insemination without stimulation approx. 75 €.
- Insemination with stimulation approx. 97 €.
- In vitro fertilisation (IVF) with embryo transfer approx. 595 €.
- Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) with embryo transfer ca. 790 €
- Anaesthesia costs approx. 150 €
- Costs for the legally insured man approx. 18 €
- Serology approx. 10 €
- Preparation of the treatment plan approx. 4 €
- In addition, there is the personal contribution for the medication: depending on the therapy, approx. 100 to 1000 € per attempt.
- The final bill is issued at the end of the treatment.
Grants from the State of Berlin / State of Brandenburg
Both the state of Berlin and the state of Brandenburg grant a subsidy for in vitro fertilisation or ICSI (intracytoplasmic sperm injection) after an application has been submitted. The Land of Berlin grants this subsidy from the 2nd attempt and also for unmarried couples. The state of Brandenburg grants this subsidy from the 1st attempt and also for unmarried couples in a stable partnership. Application forms for Berlin & application forms for Brandenburg are available for you.
For legal questions about your desire to have a child: cooperation with the lawyer Holger Eberlein.
Due to the new developments in the health care system, a certain uncertainty has arisen in some cases regarding infertility treatment, which are covered by the health insurance companies. In the event of difficulties or ambiguities, legal advice on your desire to have a child can be useful. We work together with the lawyer Holger Eberlein. Legal advice is necessary for single women and same-sex couples when using donor sperm and can also be obtained from Mr. Eberlein by telephone.












